Shoulder Labral Tear Physical Therapy Treatment
A shoulder labral tear involves partial or total separation of the labrum from the shoulder socket, often due to excessive trauma to the joint from overuse or direct injury. The labrum is a ring of cartilage that surrounds the rim of the shoulder socket, providing stability to the shoulder joint and a cushion to the shoulder during activity. Physical therapy can help those with shoulder labral tears regain strength, stability, and range of motion in the shoulder joint through manual therapy, postural training, and a stretching and strengthening exercise program.
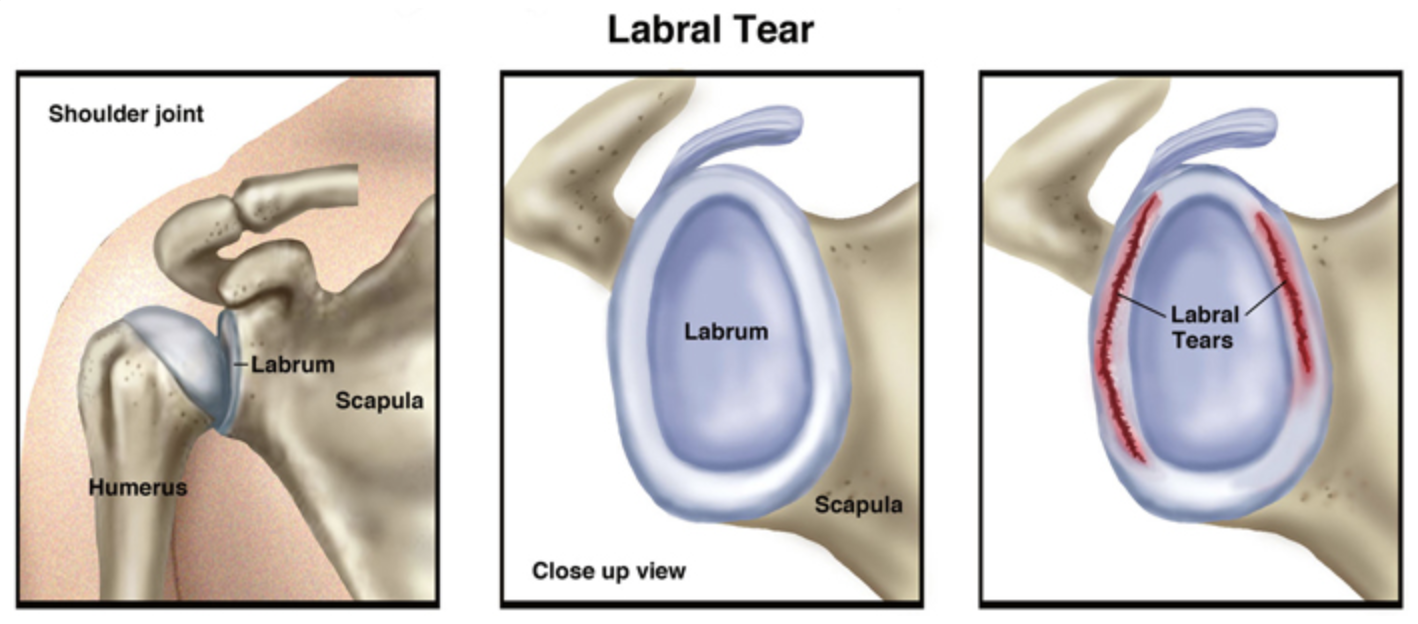
Shoulder Labrum Anatomy
The shoulder joint is comprised of the scapula (shoulder blade), the humerus (upper arm bone), and the clavicle (collarbone). The humerus bone forms a ball at the shoulder that meets the socket that is formed by the shoulder blade; the two bones are connected by ligaments. The shoulder labrum is a ring of cartilage that surrounds the rim of the shoulder socket and helps keep the ball of the humerus in place. The shoulder labrum has two main functions: 1) the labrum deepens the shoulder socket, keeping the ball of the humerus bone in place, and 2) ligaments, tendons, and muscles attach to the shoulder joint at the labrum. The labrum provides stability to the shoulder joint and helps to provide cushion to the shoulder during activity.
What is a Shoulder Labral Tear?
A labral tear in the shoulder occurs when the labrum is disrupted, frayed, or torn, leading to shoulder pain, shoulder joint instability, and in severe cases, shoulder dislocation. Labral tears can result from a fall, heavy lifting, or overuse from repetitive work activities or sports that require overhead activity, such as baseball, softball, and volleyball players and swimmers. A labral tear can also result from muscle weakness or pre-existing joint instability, which strains the shoulder capsule.
There are three types of labral tears:
When the labrum is torn completely off of the bone, which occurs when the shoulder is dislocated
When there is tearing within the labrum itself, such as the edge of the labrum becoming frayed, which occurs more often in the older population due to wear and tear
When the biceps tendon tears at the upper end of the socket, known as a SLAP tear which is more common among baseball and softball players. A SLAP tear happens then the biceps tendon pulls away from the bone and tears the labrum in the process.
Common symptoms of a labral tear include:
Pain over the top of the shoulder
Deep ache in the affected joint
Popping, “clunking,” or catching with shoulder movement. This is due to the torn labrum having “loose ends” that are flipped or rolled within the shoulder joint during arm movement. The labrum can become trapped between the upper arm bone and the shoulder blade.
Shoulder weakness and stiffness in the affected shoulder
Sensation that the shoulder joint will pop out of place
Physical Therapy Treatment for Shoulder Labral Tears
Physical therapy can help those with shoulder labral tears regain strength, stability, and range of motion in the shoulder joint. The physical therapist works to correct movement patterns that place stress on the shoulder joint and labrum and to build control, coordination, and strength in the shoulder and scapular region. If surgery is required for a severe labral tear, physical therapists play a key role in rehabilitating the repaired shoulder and helping the shoulder properly heal.
Physical therapy treatment for a shoulder labral tear can include:
Manual therapy: gentle hands-on soft tissue and joint mobilization techniques to decrease pain and help restore movement in the shoulder joint
Stretching exercises: stretching of the shoulder joint, chest, and back muscles can help improve the function of the muscles around the shoulder. Greater flexibility in these muscle groups allows the body to rotate and twist more easily without forcing the shoulder to overstretch to complete tasks like a golf swing or swinging a racquet
Strengthening exercises: targeted strengthening of the shoulder joint and scapular muscles, including the rotator cuff muscles, to decrease the stress placed on the torn labrum and improve shoulder joint stability
Core stabilization: strengthening of the core and trunk muscles to provide a solid base from which the arm and shoulder can function
Postural training: posture correction and modifications for proper positioning of the shoulder during daily activities to minimize strain on the shoulder
Dry needling: targeted dry needling of trigger points in the muscles around the shoulder, scapula, and back to improve the patient’s ability to move with decreased pain and increase range of motion that is limited due to muscle tightness
Patient education and home exercise program: patient education regarding proper technique during work and sports-related activities to minimize injury risk and a home exercise program of stretching and strengthening exercises to maintain shoulder joint function and health
Post-surgical rehabilitation: if surgery is required for a severe labral tear, a physical therapist helps to control pain and swelling during the acute phase of recovery and works with the post-operative patient to regain strength and function in the shoulder through a progressive stretching and strengthening program
A shoulder labral tear can cause shoulder joint instability and negatively affect your work and sports activities. Work with a physical therapist to address pain and dysfunction and regain strength, mobility, and range of motion in the shoulder to return to your sport or work at the highest level of function.